in this tutorial, you will learn how to work with MySQL NULL values. In addition, you’ll learn some useful functions to deal with the NULL values effectively.
Introduction to MySQL NULL values
In MySQL, a NULL value means unknown. A NULL value is different from zero or an empty string ”.Generally, you use the NULL value to indicate that the data is missing, unknown, or not applicable.When you create a table, you can specify whether a column accepts NULL values or not by using the NOT NULL constraint.
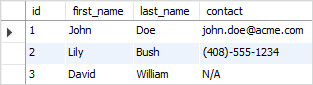
For example, the following statement creates the
leads table:
The id is the primary key column therefore, it does not accept any NULL value.
The first_name, last_name, and source columns use the NOT NULL constraint, you cannot insert any NULL values into those columns.
The email and phone columns accept NULL values.
You can use a NULL value in the INSERT statement to specify that the data is missing. For example, the following statement inserts a row into the
leads table. Because the phone number is missing, so a NULL value is provided.
Because the default value of the email column is NULL, you can omit the email in the
INSERTstatement as follows:
MySQL SET NULL in UPDATE statement
To set the value of a column to NULL, you use the assignment operator (=). For example, to update the phone of
David William to NULL, you use the following UPDATE statement:MySQL ORDER BY with NULL
If you use the ORDER BY clause to sort the result set in the ascending order, MySQL considers NULL values are lower than other values, therefore, it presents the NULL values first.
The following statement sorts the leads by phone number in ascending order.

In case you use the ORDER BY DESC, the NULL values appear at last of the result set. See the following example:

To test for NULL in a query, you use the IS NULL or IS NOT NULL operator in the WHERE clause.
For example, to get the leads who have not yet provided the phone number, you use the IS NULL operator as follows:

You can use the NOT NULL operator to get all leads who provided the email addresses.
Even though the NULL is not equal to NULL, two NULL values are equal in the GROUP BY clause.

The query returns only two rows because the rows whose email column is NULL are grouped into one.
MySQL NULL and UNIQUE index
When you use a unique constraint or a UNIQUE index on a column, you can insert multiple NULL values into that column. It is perfectly fine because in this case MySQL considers NULL values are distinct.
Let’s verify this point by creating a UNIQUE index for the phone column.
Notice that if you use the BDB storage engine, MySQL considers the NULL value are equal therefore you cannot insert multiple NULL values into a column that has a unique constraint.
MySQL NULL functions
MySQL provides several useful function that handle null values nicely: IFNULL, COALESCE, andNULLIF.
The IFNULL function accepts two parameters. The IFNULL function returns the first argument if it is not NULL, otherwise, it returns the second argument.
For example, the following statement displays the phone number if it is not known otherwise display N/A instead of NULL.

The COALESCE function accepts a list of arguments and returns the first non-NULL argument. For example, you can use the COALESCE function to display the contact information of a lead based on the priority of the information in the following order: phone, email, and N/A.
The NULLIF function accepts two arguments. If the two arguments are equal, the NULLIF function returns NULL. Otherwise, it returns the first argument.
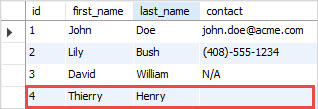
The NULLIF function is useful when both NULL and empty string values in a column. For example, by mistake, you insert a following row into the leads table:
The phone is an empty string instead of a NULL value.
If you want to get the contact information of leads, you end up with an empty phone instead of the email as the following query
To fix this, you use the NULLIF function to compare the phone with the empty string, if they are equal, it returns NULL, otherwise it returns the phone number.

In this tutorial, you have learned how to work with MySQL NULL values and how to use some handy functions to handle NULL values in the queries.

1 comment:
commentgood
Reply